Unix-like os 基础知识笔记
2 CPU Sheduling
2.1 调度指标 (sheduling policy)
- turnaround time 周转时间, 任务完成时间减去到达时间
- response time 响应时间, 任务首次运行时间减去到达时间
- fairness 公平性
轮转 (Round-Robin) 在一个时间片 (time slice), 有时称为调度量子 (scheduling quantum) 内运行一个工作, 然后切换到运行队列中的下一个任务
2.2 多级反馈队列 (Multi-level Feedback Queue)
有多级队列, 并利用反馈信息决定某个工作的优先级
- 如果 A 的优先级 > B 的优先级, 运行 A
- 如果 A 的优先级 = B 的优先级, 轮转运行 A 和 B
- 工作进入系统时, 放在最高优先级
- 一旦工作用完了其在某一层中的时间配额, 就降低其优先级, 移入低一级队列
- 经过一段时间 S, 就将系统中所有工作重新加入最高优先级队列
2.3 比例份额 (proportional-share)
确保每个工作获得一定比例的 CPU 时间, 而不是优化周转时间和响应时间, 如彩票调度 (lottery scheduling)
步长调度 (stride scheduling) 一个确定性的公平分配算法, 每个工作都有自己的步长, 这个值与票数值成反比, 进行调度时, 选择目前拥有最小行程值的进程, 并且在运行之后将该进程的行程值增 加一个步长
current = remove_min(queue); // pick client with minimum pass schedule(current); // use resource for quantum current->pass += current->stride; // compute next pass using stride insert(queue, current); // put back into the queue
2.4 单/多队列调度 (Single/Multi Queue Multiprocessor Scheduling)
- 单队列的方式 (SQMS) 比较容易构建, 负载均衡较好, 但在扩展性和缓存亲和度方面有着固有的缺陷
- 多队列的方式 (MQMS) 有很好的扩展性和缓存亲和度, 但实现负载均衡却很困难
2.5 实时调度器 (Real-time Schduler) 和公平调度器 (Completely Fair Scheduler)
linux 将线程分为三类: 实时先入先出, 实时轮转, 分时, 实时的优先级为 0 ~ 99, 非实时的优先级为 100 ~ 139, nice -20对应100, nice 19对应139
- 处理实时任务的实时调度器 (Real-time Schduler)
- 处理非实时任务的默认调度器: 公平调度器 (Completely Fair Scheduler)
- 根据任务在 CPU 上运行时间的长短 (虚拟运行时间 vruntime) 排列在一个红黑树上, 优先调度 vruntime 小的任务, 优先级较低的任务 vruntime 会增加的更快
- 调度器只考虑可以运行的任务, 其他任务被放入等待队列中, 等待队列包含了一个自旋锁
3 Memory
3.1 物理内存
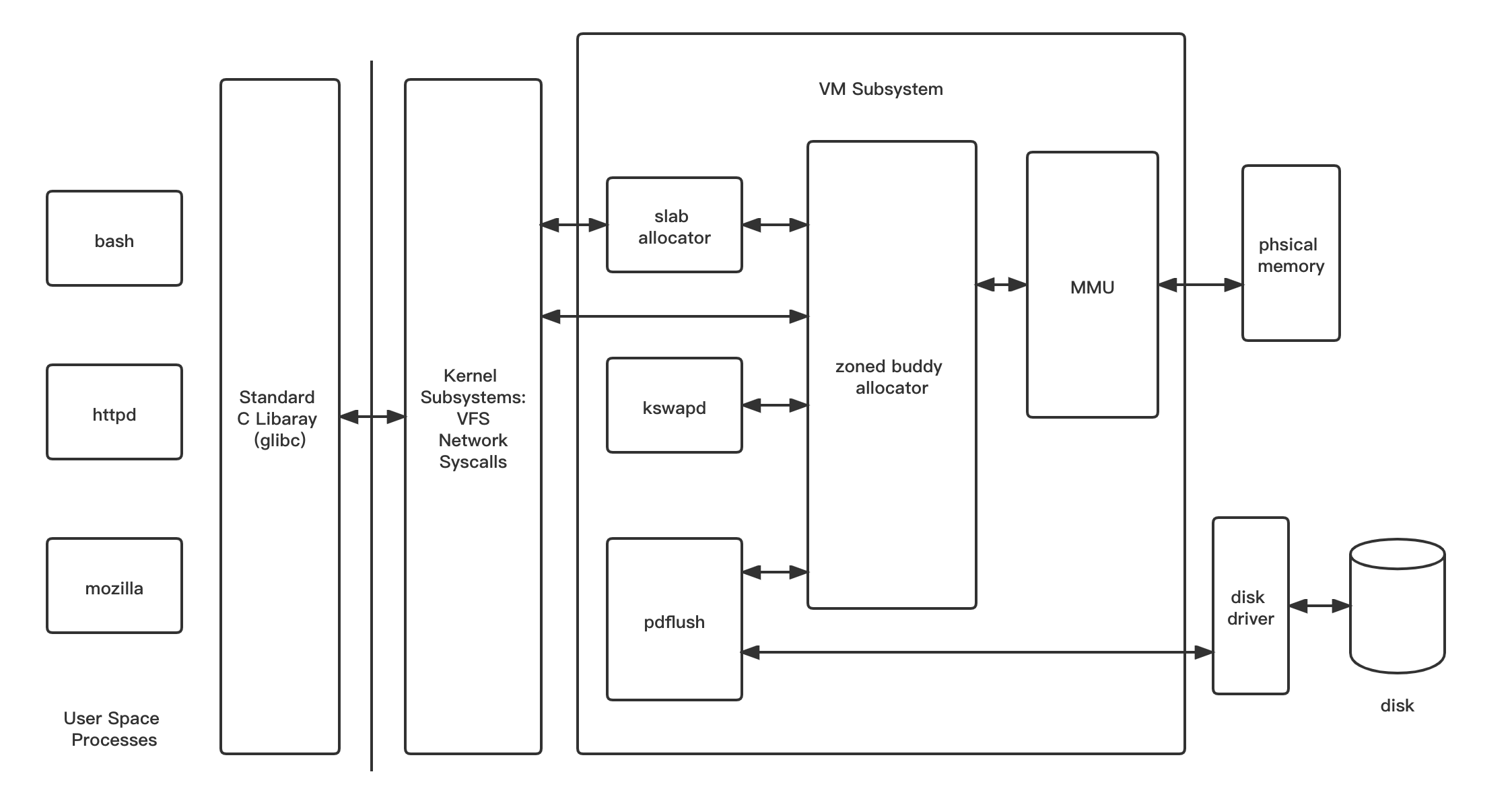
如下图, 在 NUMA 机器上, 每个 NUMA node 都有一个 pg_data_t 来描述它的内存布局, 在 UMA 机器上, 有一个描述整个内存的 pglist_data; 内存统计和页面替换数据结构是按 zone 维护的; page 结构体表示一个 4k 大小的物理页, 也叫页框
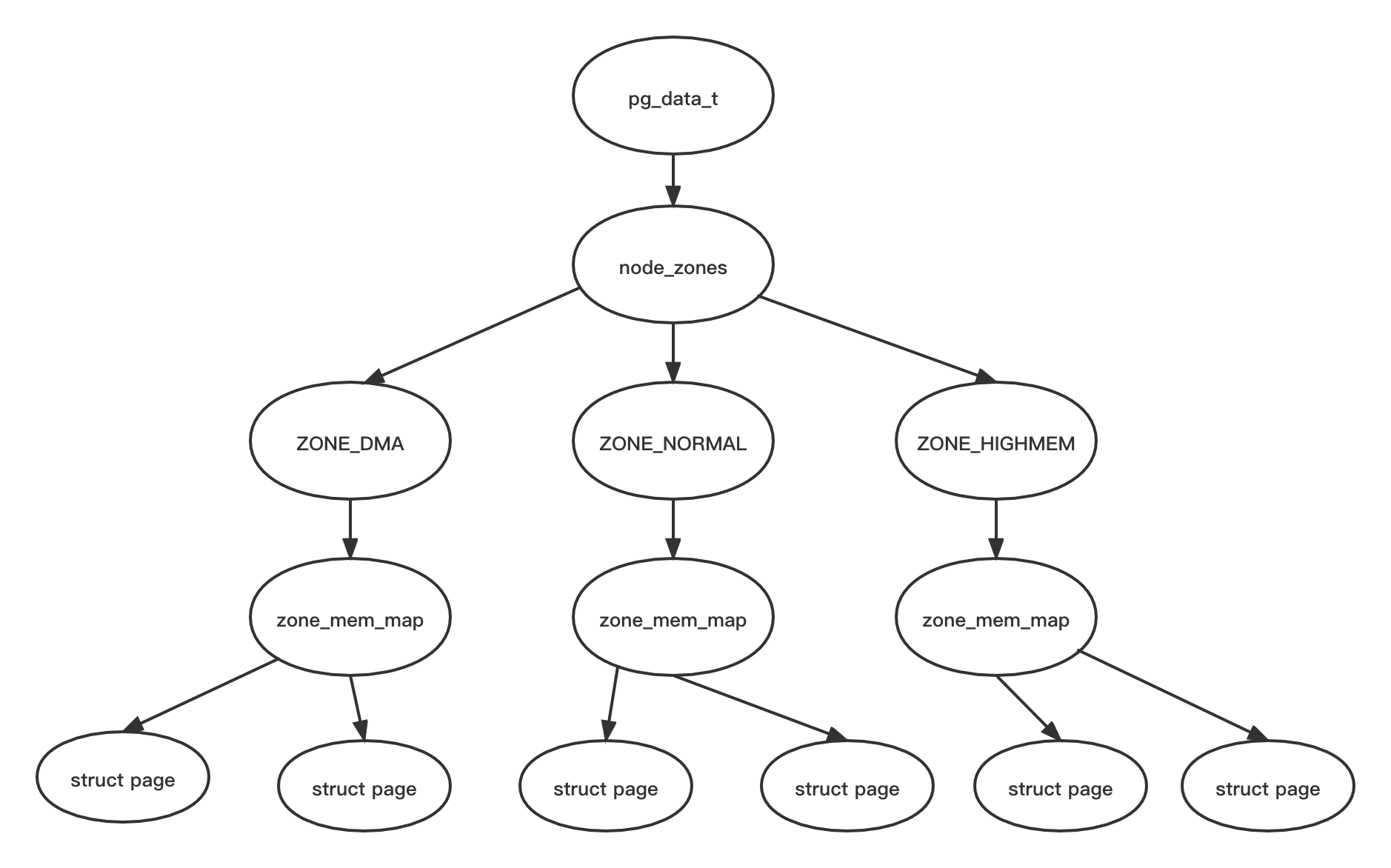
3.1.1 伙伴算法 (buddy system)
伙伴算法把空闲的页框分组为 11 个块链表, 在第 i 个链表中每个页框块包含 2 的 i-1 次方个连续的页框
/* 分配 2^order 个连续的物理页, 返回一个指针指向第一个物理页的 page 结构体 */ static inline struct page *alloc_pages(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order) /* 返回 page 所映射的虚拟地址 */ void *page_address(const struct page *page)
分配时, 可能需要将大块内存拆分成两个小伙伴; 释放时, 可能会将两个小伙伴合并再次组成更大块的连续内存
伙伴系统通过迁移类型实现反碎片化, 迁移类型为 Unmovable 的页面都聚集在 order < 3 时,说明碎片化严重
3.1.2 kvmalloc
在伙伴算法的基础上有两种分配内存的机制: slab 和 vmalloc, slab 分配物理上小而连续的内存, vmalloc 分配物理上大而不连续的内存
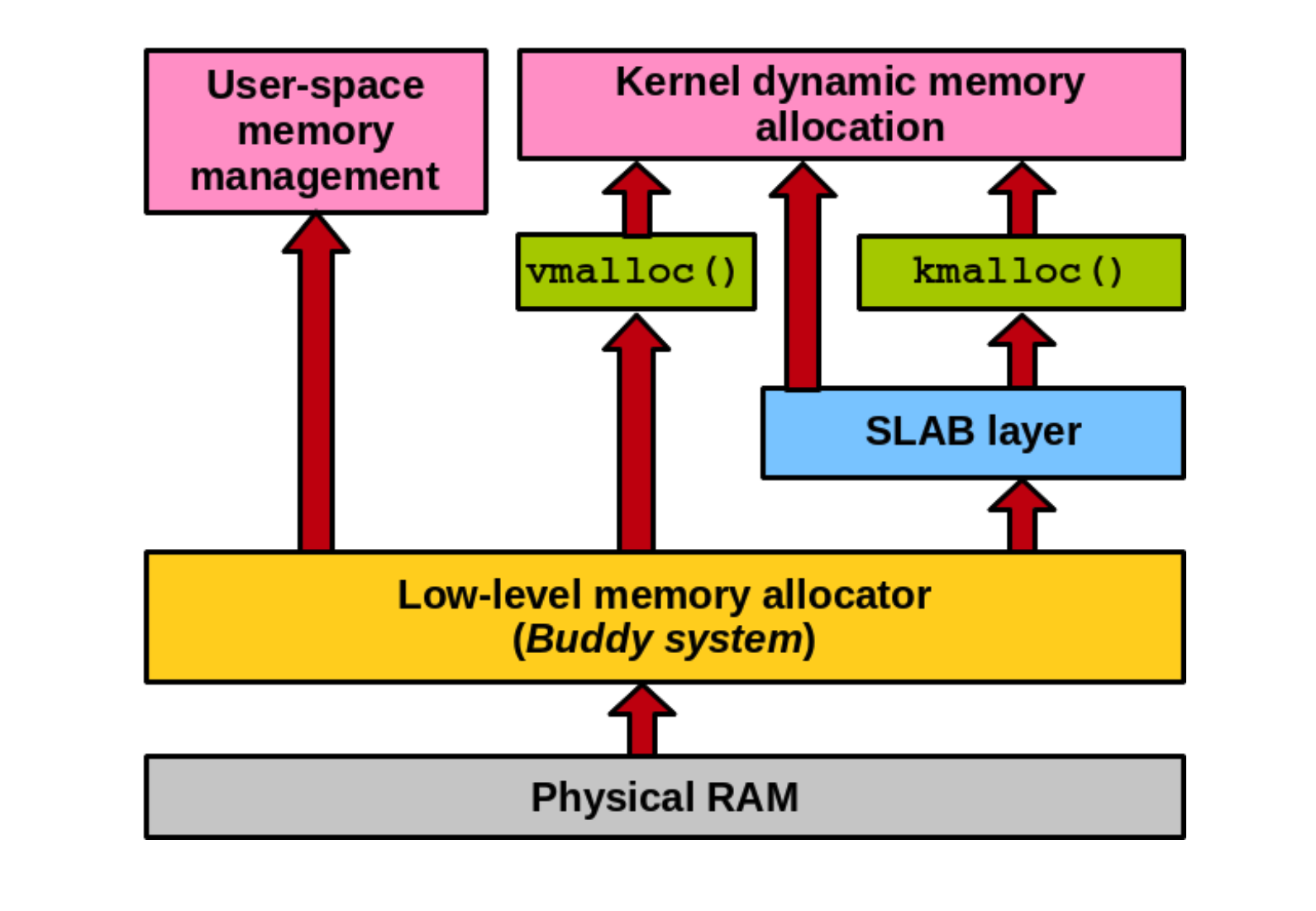
kvmalloc 先尝试使用 slab 进行分配, 如果不成功就使用 vmalloc 来分配
memory = kmalloc(allocation_size, GFP_KERNEL); if (!memory) memory = vmalloc(allocation_size);
3.1.3 slab
slab 减少伙伴算法在分配小块连续内存时产生的内部碎片, 将频繁使用的对象缓存起来, 通过着色技术调整对象以更好的使用硬件高速缓存
有三种 slab allocator:
- slob: 适用于小型系统, 使用简单的 first-fit 算法, 追求 as compact as possible
- slab: 来自 Solaris 系统, 追求 as cache friendly as possible
- slub: 适用于大型系统, 减小了 memory overhead, linux 默认的 allocator, 追求 simple and instruction cost counts, defragmentation, execution time friendly
这三者间的更多比较可见 Slab allocators in the Linux Kernel: SLAB, SLOB, SLUB Christoph Lameter
3.1.4 commands
- dmidecode 查看内存条, 每一个 CPU 以及和他直连的内存条组成了一个 node 节点
- cat /proc/buddyinfo : 伙伴系统里可用内存的情况
- cat /proc/pagetypeinfo : 伙伴系统里可用内存的情况 (分类型)
- cat /proc/slabinfo : objperslab (一个 slab 里存放的对象的数量), pagesperslab (一个slab 占用的页面的数量)
- slabtop
- sar -B
- cat /sys/kernel/debug/extfrag/extfrag_index 碎片化情况
3.2 虚拟内存
- performance goals
- throughput: number of completed requests per unit time
- peak memory utilization = max_playload / heap_size
- placement policy, splitting policy, coalescing policy
- placement policy
- 首次适配从头开始搜索空闲链表, 选择第一个合适的空闲块
- 下一次适配从上一次查询结束的地方开始开始搜索空闲链表
- 最佳适配检查每个空闲块, 选择适合所需请求大小的最小空闲块
3.2.1 dlmalloc
dlmalloc 是一款 general-purpose allocator, 主要的数据结构如下 (version 2.7.0)
struct malloc_state {
/* The maximum chunk size to be eligible for fastbin */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T max_fast; /* low 2 bits used as flags */
/* Fastbins */
mfastbinptr fastbins[NFASTBINS];
/* Base of the topmost chunk -- not otherwise kept in a bin */
mchunkptr top;
/* The remainder from the most recent split of a small request */
mchunkptr last_remainder;
/* Normal bins packed as described above */
mchunkptr bins[NBINS * 2];
/* Bitmap of bins */
unsigned int binmap[BINMAPSIZE];
/* Tunable parameters */
unsigned long trim_threshold;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T top_pad;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T mmap_threshold;
/* Memory map support */
int n_mmaps;
int n_mmaps_max;
int max_n_mmaps;
/* Cache malloc_getpagesize */
unsigned int pagesize;
/* Statistics */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T mmapped_mem;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T sbrked_mem;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T max_sbrked_mem;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T max_mmapped_mem;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T max_total_mem;
};
- boundary tags
边界标签保存了每个 chunk 的一些信息, 以便于两个相邻的 free chunk 的合并, 可以从任何已知的块开始向前或向后遍历所有块
struct malloc_chunk { INTERNAL_SIZE_T prev_size; /* Size of previous chunk (if free). */ INTERNAL_SIZE_T size; /* Size in bytes, including overhead. */ struct malloc_chunk* fd; /* double links -- used only if free. */ struct malloc_chunk* bk; }; - binning
分箱表示相同大小的 free chunk 连成的一个 bin, dlmalloc 默认使用 best-fit 去搜索最合适的分箱, 但为了追求局部性来减少 page fault 和 cache miss, 某些情况下会使用 nearest-fit 或 next-fit
- caching
dlmalloc 中使用了 deferred coalescing 延迟合并 和 preallocation 预分配这两种缓存策略
3.2.2 ptmalloc
ptmalloc 派生自 dlmalloc, 有一个主分配区 (main arena), 多个非主分配区 (thread arena), 非主分配区只能使用 mmap(2) 申请虚拟内存
bin 分为 fast bin (包含最近释放的小块, 使用更快的单链表, 使用更快的 LIFO, 相邻的 free chunk 不合并), unsorted bin (来自块拆分的剩余部分, 提供一次在分箱前使用的机会), small bin 和 large bin
chunk 分为 allocated chunk, free chunk, top chunk (也称 wilderness) 和 last remainder chunk
- Allocated chunk:
- prev_size: If the previous chunk is free, this field contains the size of previous chunk. Else if previous chunk is allocated, this field contains previous chunk’s user data.
- size: This field contains the size of this allocated chunk. Last 3 bits of this field contains flag information.
- PREV_INUSE (P) – This bit is set when previous chunk is allocated.
- IS_MMAPPED (M) – This bit is set when chunk is mmap’d.
- NON_MAIN_ARENA (N) – This bit is set when this chunk belongs to a thread arena.
- Free chunk:
- prev_size: No two free chunks can be adjacent together. When both the chunks are free, its gets combined into one single free chunk. Hence always previous chunk to this freed chunk would be allocated and therefore prev_size contains previous chunk’s user data.
- size: This field contains the size of this free chunk.
- fd: Forward pointer – Points to next chunk in the same bin (and NOT to the next chunk present in physical memory).
- bk: Backward pointer – Points to previous chunk in the same bin (and NOT to the previous chunk present in physical memory).
- Top chunk: Chunk which is at the top border of an arena is called top chunk. It doesnt belong to any bin.
- Last Remainder chunk: Last remainder chunk helps to improve locality of reference ie) consecutive malloc request of small chunks might end up being allocated close to each other.
3.3 物理内存与虚拟内存的映射
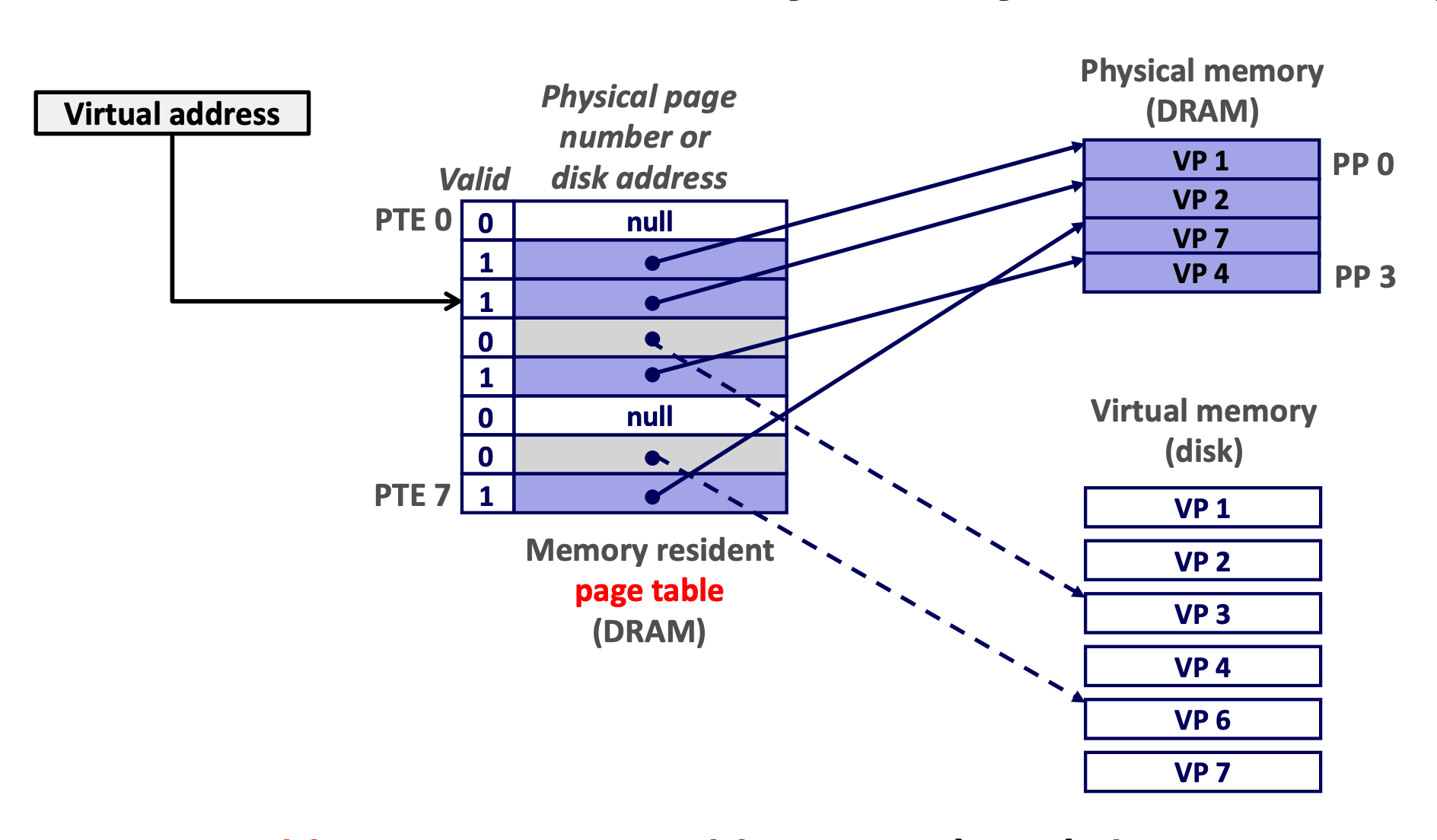
3.3.1 分页
multi-level page tables
- PGD:page global directory (47-39), 页全局目录, 查看大小: getconf PAGE_SIZE = 4096
- PUD:page upper directory (38-30), 页上级目录
- PMD:page middle directory (29-21), 页中间目录
- PTE:page table entry (20-12), 页表项
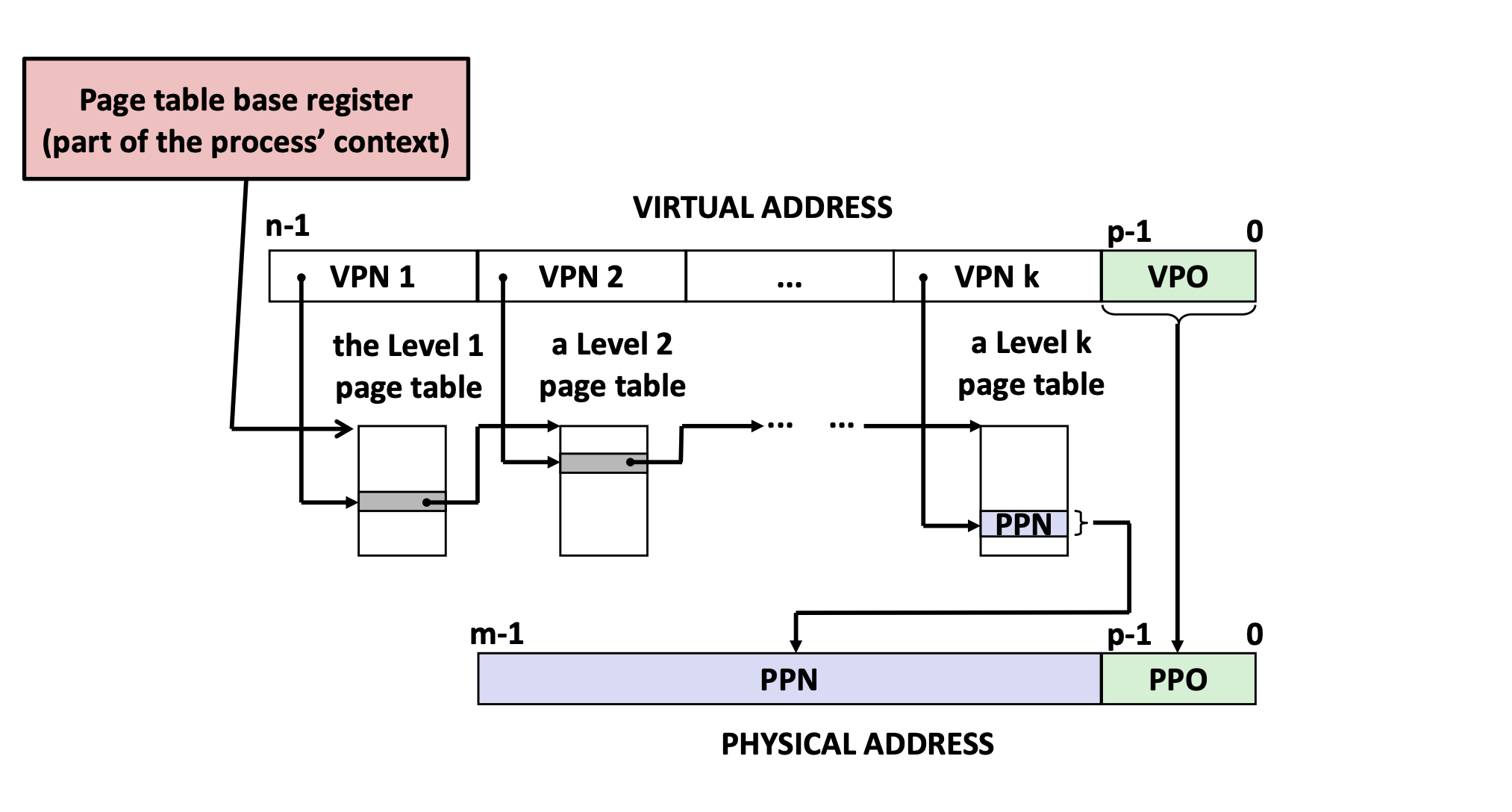
Figure 5: k-level page (source: CSAPP) - Page Table Base Register: CR3 寄存器保存着当前进程页目录的物理地址, 切换进程就会改变 CR3 的值 (part of the process' context)
- memory protection
- extend PTEs with permission bits (sup, read, write, exec)
- 64位的地址只使用了低48位, 高位全为1的是用于内核, 高位全为0的是用于用户
components of the virtual address (VA)
- TLBI: TLB index
- TLBT: TLB tag
- VPO: virtual page offset
- VPN: virtual page number
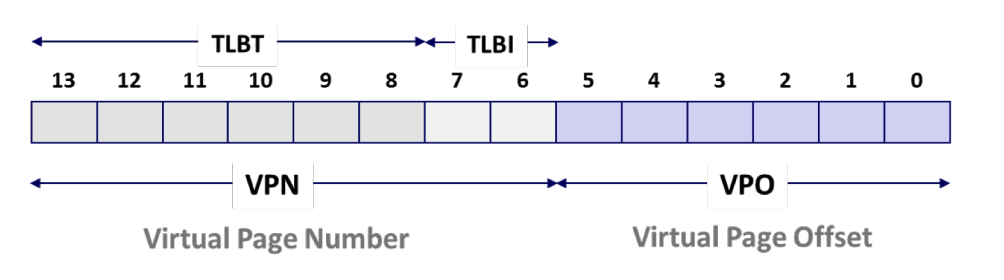
Figure 6: virtual address (source: CSAPP) components of the physical address (PA)
- PPO: physical page offset
- PPN: physical page number
- CO: byte offset within cache line
- CI: cache index
- CT: cache tag
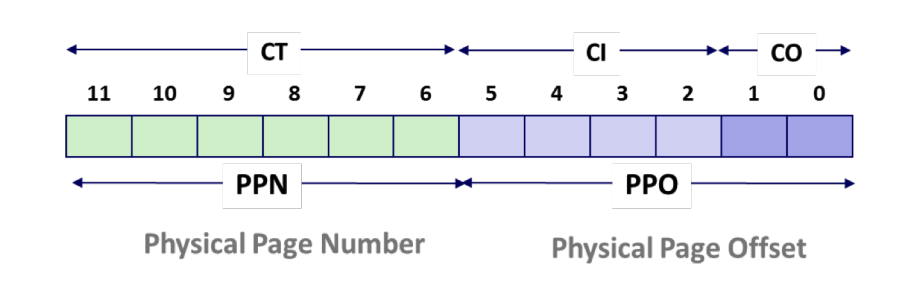
Figure 7: physical address (source: CSAPP)
3.3.2 TLB (Translation Lookaside Buffer)
TLB miss 后才会去 multi-level page tables 中寻找 PPN
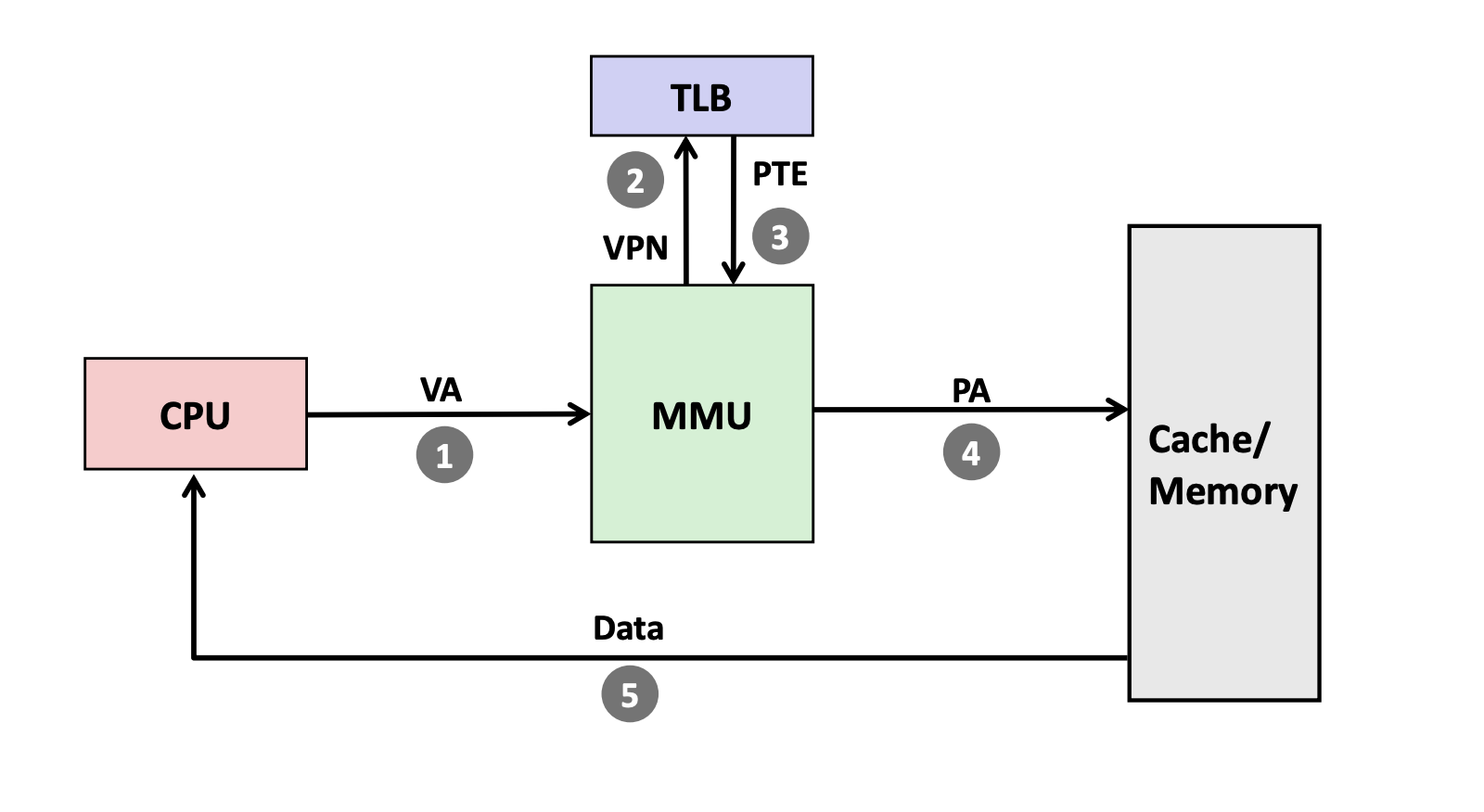
Figure 8: TLB (source: CSAPP) VPN = (VirtualAddress & VPN_MASK) >> SHIFT (Success, TlbEntry) = TLB_Lookup(VPN) if (Success == True) // TLB Hit if (CanAccess(TlbEntry.ProtectBits) == True) Offset = VirtualAddress & OFFSET_MASK PhysAddr = (TlbEntry.PFN << SHIFT) | Offset AccessMemory(PhysAddr) else RaiseException(PROTECTION_FAULT) else // TLB Miss PTEAddr = PTBR + (VPN * sizeof(PTE)) PTE = AccessMemory(PTEAddr) if (PTE.Valid == False) RaiseException(SEGMENTATION_FAULT) else if (CanAccess(PTE.ProtectBits) == False) RaiseException(PROTECTION_FAULT) else TLB_Insert(VPN, PTE.PFN, PTE.ProtectBits) RetryInstruction()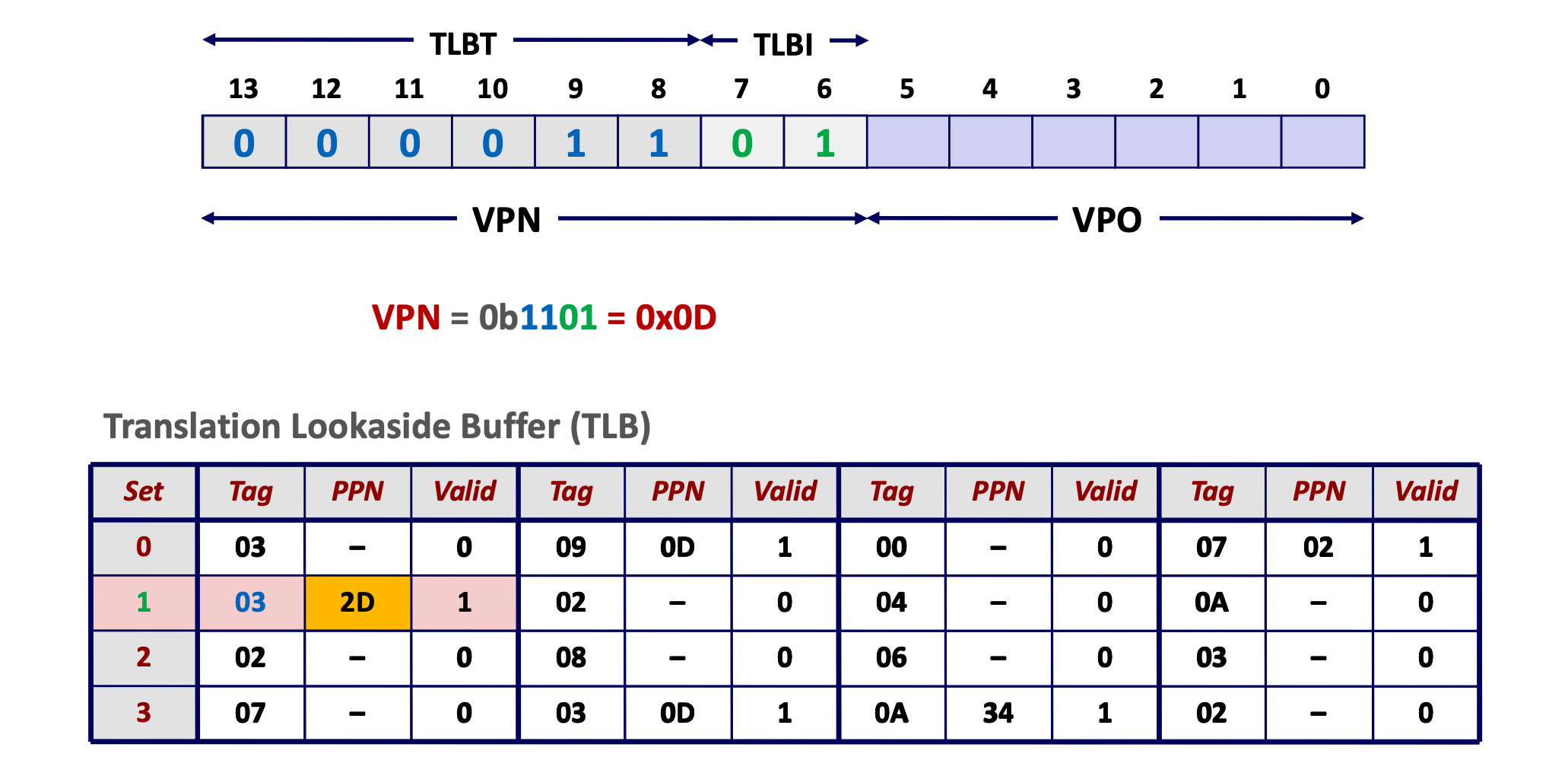
Figure 9: TLB example (source: CSAPP) 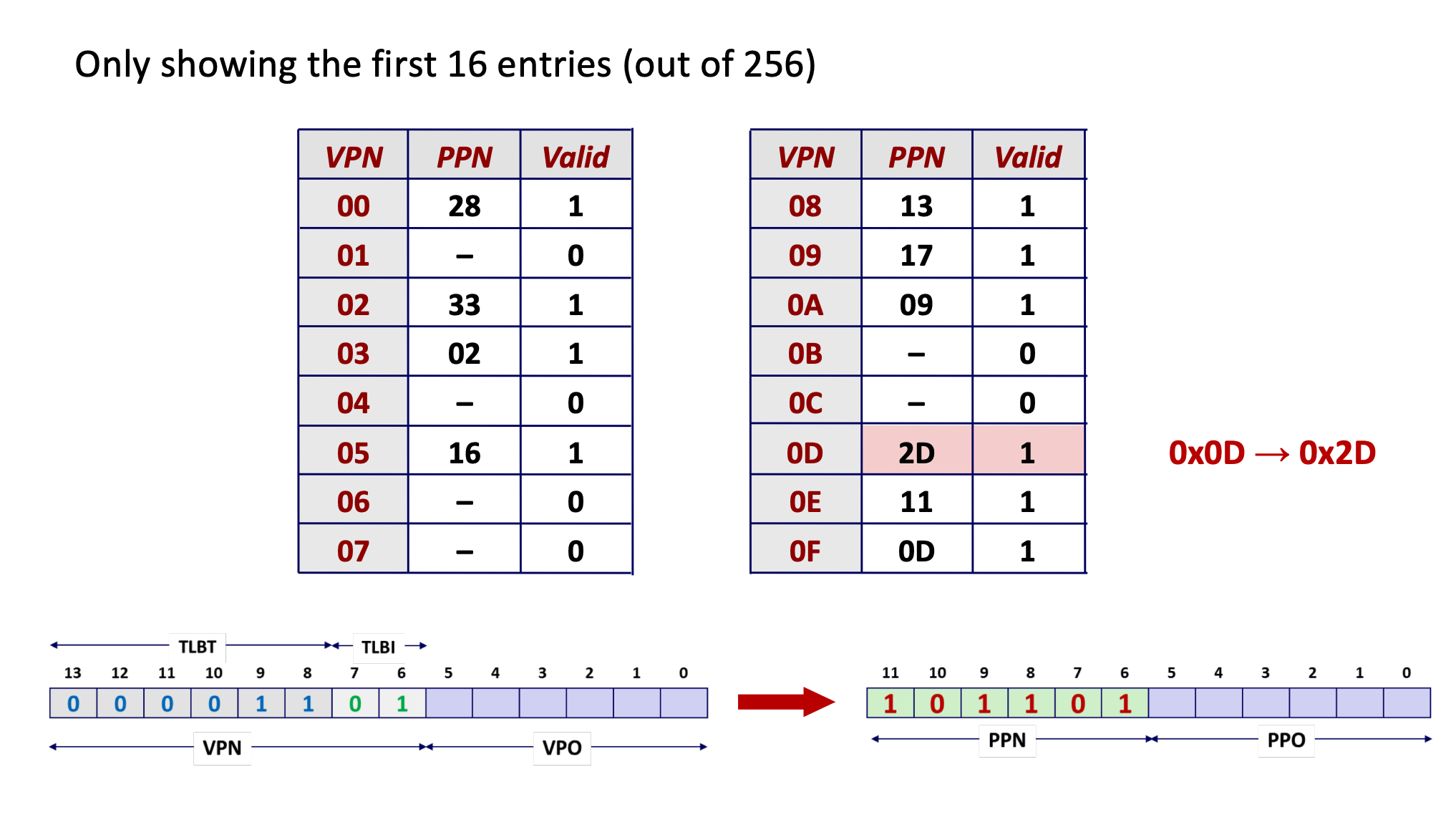
Figure 10: TLB example (source: CSAPP) - CISC (Complex-Instruction Set Computer) 由硬件全权处理 TLB miss, 而 RISC (Reduced-Instruction Set Computer) 通过 trap handler 进行处理
- ASID (Address Space Identifier) TLB 中的地址空间标识符, 标识了是哪个进程的映射, 使得 TLB 可以同时缓存不同进程的地址空间映射
4 Control Flow
4.1 exceptional control flow
- asynchronous exceptions (interrputs)
- cause by events external to the processor, such as timer interrput
- synchronous exceptions
- traps
- international, example: system calls
- faults
- uninternational but possibly recoverable, example: page faults
- aborts
- uninternational and unrecoverable
4.2 process
#include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/wait.h> pid_t fork(void); void _exit(int status); pid_t wait(int *status); pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid, int *status, int options); pid_t wait3(int *status, int options, struct rusage *rusage); pid_t wait4(pid_t pid, int *status, int options, struct rusage *rusage); int execve(const char *filename, char *const argv[], char *const envp[]);
- pid_t pid: 通过 syscall(SYS_gettid) 获取
- pid_t tgid: thread group id, clone(2) 中的 CLONE_THREAD 可将其设为父进程的 tgid, 可以通过 getpid(2) 获取
- 有两套 signal_pending , 一套是线程组共享的, 一套是线程独有的
- 僵尸进程: 子进程退出, 父进程并没有调用 waitpid, 子进程的进程描述符仍然保存在系统中
孤儿进程: 父进程退出, 它的子进程还在运行, 那么那些子进程将成为孤儿进程, 孤儿进程将被 init 进程 (进程号为1) 所收养
#include <unistd.h> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <stdio.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { if (fork() == 0) { if (fork()) { printf("parent exit\n"); exit(0); } sleep(2); printf("orphan process' parent tgid = %d\n", getppid()); exit(0); } printf("parent parent exit\n"); return 0; }vfork(2) 用于节省拷贝进程数据调用, vfork(2) 实际上借用了父进程的空间, vfork(2) 创建的子进程应该马上调用 execve(2) 或 _exit(2)
#include <unistd.h> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <stdio.h> int a = 4; int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int b = 6; printf("before vfork\n"); if (vfork() == 0) { a++; b++; _exit(0); } printf("pid = %d, a = %d, b = %d\n", getpid(), a, b); return 0; }exec(3) 有多种, 并最终调用 execve(2)
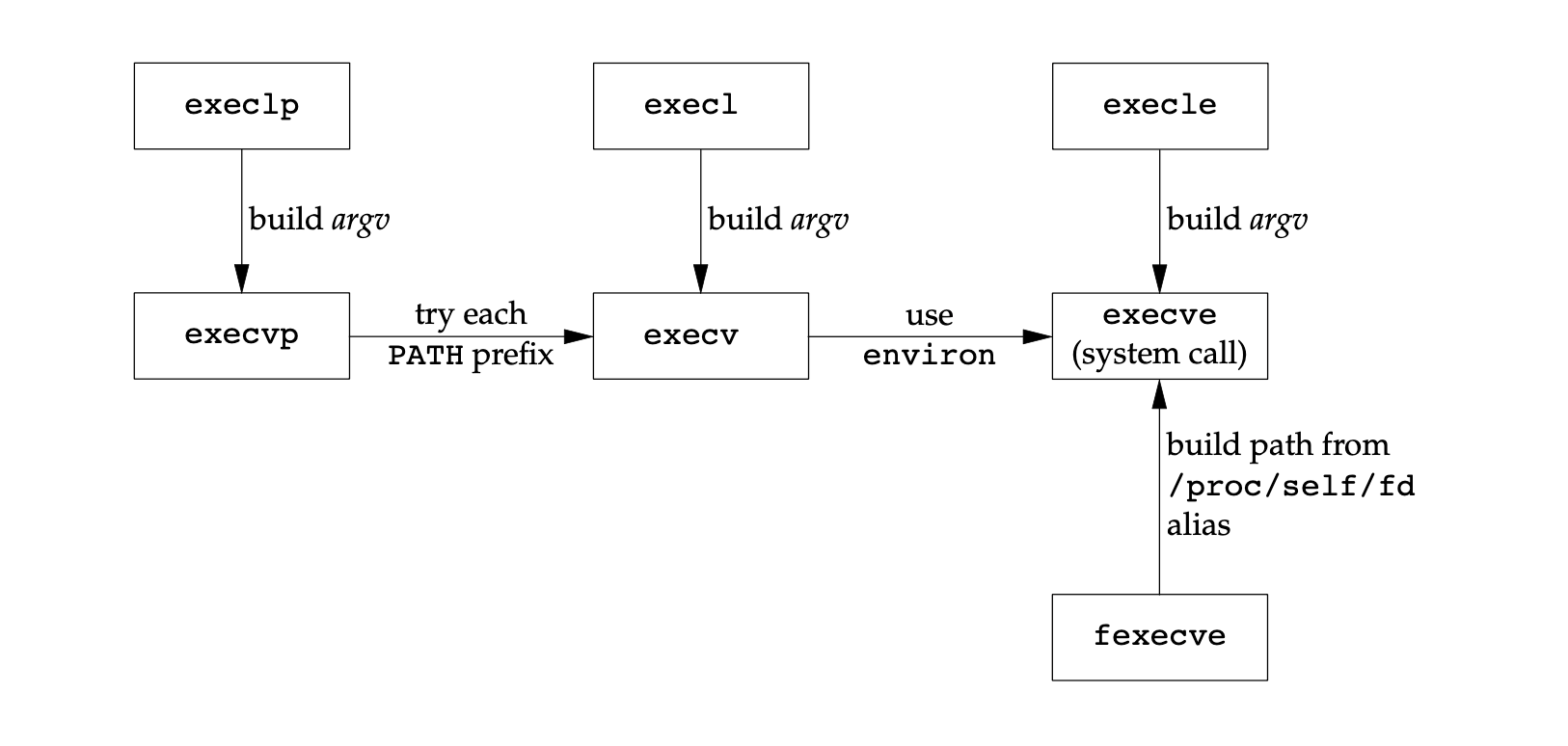
Figure 11: relationship of exec functions (source: APUE) l: 可变参数 const char *arg
execl("/bin/ls", "ls", "-l", NULL);v: 参数列表 char *const argv[]
int ret; char *argv[] = {"ls", "-l", NULL}; ret = execvp("ls", argv);e: 传递环境变量 char *const envp[]
extern char **environ;
p: 第一个参数 path 不用输入完整路径, 只有给出命令名即可, 它会在环境变量 PATH 当中查找命令
execlp("ls", "ls", "-l", NULL);
4.3 thread
4.3.1 thread-local storage
thread-local storage 为段寄存器 FS/GS 指向的一块内存, 由 clone(2) 中的 newtls 参数传给 FS/GS, 为 struct pthread 的变量 pd 的地址
#include <sched.h>
int clone(int (*fn)(void *), void *child_stack, int flags, void *arg, ...
/* pid_t *ptid, void *newtls, pid_t *ctid */ );
4.3.2 barrier
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_barrier_init(pthread_barrier_t *restrict barrier,
const pthread_barrierattr_t *restrict attr, unsigned count);
int pthread_barrier_wait(pthread_barrier_t *barrier);
int pthread_barrier_destroy(pthread_barrier_t *barrier);
pthread_barrier_init 设置屏障计数 count, 调用 pthread_barrier_wait 的线程在未达到屏障计数时都会进入睡眠, 屏障计数满足后全部线程将被唤醒
4.4 signal
signal(2) 设置信号处理函数, kill(2) 发送信号, pause(2) 等待信号
#include <signal.h> sighandler_t signal(int signum, sighandler_t handler); typedef void (*__sighandler_t) (int); #define SIG_ERR ((__sighandler_t) -1) /* Error return. */ #define SIG_DFL ((__sighandler_t) 0) /* Default action. */ #define SIG_IGN ((__sighandler_t) 1) /* Ignore signal. */ int kill(pid_t pid, int sig); int pause(void);
可以使用 sigaction(2) 实现 signal
int sigaction(int signum, const struct sigaction *act, struct sigaction *oldact);
struct sigaction {
void (*sa_handler)(int);
void (*sa_sigaction)(int, siginfo_t *, void *);
sigset_t sa_mask;
int sa_flags;
void (*sa_restorer)(void);
};
typedef void (*sighandler_t)(int);
sighandler_t signal2(int signum, sighandler_t handler) {
struct sigaction act, oldact;
act.sa_handler = handler;
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
act.sa_flags = 0;
if (signum == SIGALRM)
act.sa_flags |= SA_INTERRUPT;
else
act.sa_flags |= SA_RESTART;
if (sigaction(signum, &act, &oldact) < 0)
return(SIG_ERR);
return(oldact.sa_handler);
}
可以使用 alarm(2) 实现 sleep, 但未处理与以前设置的闹钟的相互作用
#include <signal.h>
void sigalrm_handler(int signum) {
}
unsigned int sleep2(unsigned int seconds) {
struct sigaction act, oldact;
sigset_t mask, oldmask, suspmask;
unsigned int unslept;
/* set action */
act.sa_handler = sigalrm_handler;
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
act.sa_flags = 0;
sigaction(SIGALRM, &act, &oldact);
/* set mask */
sigemptyset(&mask);
sigaddset(&mask, SIGALRM);
sigprocmask(SIG_BLOCK, &mask, &oldmask); /* block SIGALRM */
alarm(seconds);
/* make sure SIGALRM isn't blocked */
suspmask = oldmask;
sigdelset(&suspmask, SIGALRM);
sigsuspend(&suspmask); /* wait for any signal to be caught */
unslept = alarm(0);
sigaction(SIGALRM, &oldact, NULL); /* reset previous action */
sigprocmask(SIG_SETMASK, &oldact, NULL); /* reset signal mask */
return(unslept);
}
5 I/O
5.1 file I/O
#include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h> #include <fcntl.h> int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode); int creat(const char *pathname, mode_t mode); /* equivalent to open(pathname, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, mode) */ off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence); int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, ... /* arg */ ); int ioctl(int d, int request, ...); ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count); /* return 0 indicates end of file, -1 indicates error */ ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count); int fsync(int fd);
pread(2)/pwrite(2) 将 lseek(2) 和 read(2)/write(2) 合并成一个原子操作
ssize_t pread(int fd, void *buf, size_t count, off_t offset); ssize_t pwrite(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count, off_t offset);
5.2 standard I/O
对流的操作
#include <stdio.h> int fileno(FILE *stream); FILE *fopen(const char *path, const char *mode); int fclose(FILE *fp); int fflush(FILE *stream); int fseek(FILE *stream, long offset, int whence); void rewind(FILE *stream); /* equivalent to (void) fseek(stream, 0L, SEEK_SET) */
输入 getc(3) 可能使用宏来实现, 而 fgetc(3) 只可能是函数
int getc(FILE *stream); int fgetc(FILE *stream); int getchar(void); /* equivalent to getc(stdin) */ char *fgets(char *s, int size, FILE *stream); /* A terminating null byte ('\0') is stored after the last character in the buffer */ size_t fread(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream);使用 ferror(3) 和 feof(3) 判断是出错还是到达文件尾端
int ferror(FILE *stream); int feof(FILE *stream); void clearerr(FILE *stream);
输出 putc(3) 可能使用宏来实现, 而 fputc(3) 只可能是函数
int putc(int c, FILE *stream); int fputc(int c, FILE *stream); int putchar(int c); /* equivalent to putc(stdout) */ int fputs(const char *s, FILE *stream); size_t fwrite(const void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream);
5.2.1 缓冲
使用 setbuf(3) 或 setvbuf(3) 可以将一个文件流设为全缓冲 (_IOFBF), 行缓冲 (_IOLBF) 或不带缓冲 (_IONBF)
#include <stdio.h> void setbuf(FILE *stream, char *buf); int setvbuf(FILE *stream, char *buf, int mode, size_t size);
默认情况下, 标准输入输出连至终端时是行缓冲的, 重定向到普通文件时是全缓冲的
5.3 poll (file_operations)
文件操作中的 poll 操作会将当前进程的 task_struct 加入设备驱动的等待队列, 并设置回调函数, 检查已发生的事件 (可读, 可写, 异常)
struct file_operations {
/* ... */
__poll_t (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *);
/* ... */
};
typedef struct poll_table_struct {
poll_queue_proc _qproc;
__poll_t _key;
} poll_table;
typedef void (*poll_queue_proc)(struct file *, wait_queue_head_t *, struct poll_table_struct *);
struct wait_queue_head {
spinlock_t lock;
struct list_head head;
};
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};
6 Concurrency
6.1 spinlock
评价一个锁主要有三方面: correctness, fairness, performance
6.1.1 compare and swap
int CompareAndSwap(int *ptr, int expected, int newval) {
int actual = *ptr;
if (actual == expected)
*ptr = newval;
return actual;
}
typedef struct __lock_t {
int flag;
} lock_t;
void init(lock_t *lock) {
// 0 indicates that lock is available, 1 that it is held
lock->flag = 0;
}
void lock(lock_t *lock) {
while (CompareAndSwap(&lock->flag, 0, 1) == 1)
; // spin-wait (do nothing)
}
void unlock(lock_t *lock) {
lock->flag = 0;
}
char compare_and_swap(int *ptr, int oldval, int newval) {
unsigned char ret;
// Note that sete sets a ’byte’ not the word
__asm__ __volatile__ (
" lock\n"
" cmpxchgl %2,%1\n"
" sete %0\n"
: "=q" (ret), "=m" (*ptr)
: "r" (newval), "m" (*ptr), "a" (oldval)
: "memory");
return ret;
}
CAS 保证了 correctness, 但没有实现 fairness, 可能导致某个线程等待了很久一直没有抢到锁
6.1.2 fetch and add
int FetchAndAdd(int *ptr) {
int old = *ptr;
*ptr = old + 1;
return old;
}
typedef struct lock_t {
int ticket;
int turn;
} lock_t;
void lock_init(lock_t *lock) {
lock->ticket = 0;
lock->turn = 0;
}
void lock(lock_t *lock) {
int myturn = FetchAndAdd(&lock->ticket);
while (lock->turn != myturn)
; // spin
}
void unlock(lock_t *lock) {
FetchAndAdd(&lock->turn);
}
fetch and add 保证了一定的 fairness, 先等待的线程获得的更小的 myturn, 这样也会更早地达成 lock->turn == myturn, 获取锁
但有两个问题, 一是当 turn 的值没有变化时仍会不断地自旋检查, 二是当值变化时, CPU cache 中的值会放入 invalidate queue (MESI protocol), 但只有获取锁的 CPU 的这步操作有意义
6.1.3 solaris 使用 park 睡眠在队列上代替自旋
int TestAndSet(int *old_ptr, int newval) {
int old = *old_ptr; // fetch old value at old_ptr
*old_ptr = newval; // store 'newval' into old_ptr
return old; // return the old value
}
typedef struct lock_t {
int flag;
int guard;
queue_t *q;
} lock_t;
void lock_init(lock_t *m) {
m->flag = 0;
m->guard = 0;
queue_init(m->q);
}
void lock(lock_t *m) {
while (TestAndSet(&m->guard, 1) == 1)
; //acquire guard lock by spinning
if (m->flag == 0) {
m->flag = 1; // lock is acquired
m->guard = 0;
} else {
queue_add(m->q, gettid());
setpark(); // avoid wakeup/waiting race
m->guard = 0;
park();
}
}
void unlock(lock_t *m) {
while (TestAndSet(&m->guard, 1) == 1)
; //acquire guard lock by spinning
if (queue_empty(m->q))
m->flag = 0; // let go of lock; no one wants it
else
unpark(queue_remove(m->q)); // hold lock (for next thread!)
m->guard = 0;
}
6.1.4 linux futex
void mutex_lock (int *mutex) {
int v;
/* Bit 31 was clear, we got the mutex (this is the fastpath) */
if (atomic_bit_test_set (mutex, 31) == 0)
return;
atomic_increment (mutex);
while (1) {
if (atomic_bit_test_set (mutex, 31) == 0) {
atomic_decrement (mutex);
return;
}
/* We have to wait now. First make sure the futex value
we are monitoring is truly negative (i.e. locked). */
v = *mutex;
if (v >= 0)
continue;
futex_wait (mutex, v);
}
}
void mutex_unlock (int *mutex) {
/* Adding 0x80000000 to the counter results in 0 if and only if
there are not other interested threads */
if (atomic_add_zero (mutex, 0x80000000))
return;
/* There are other threads waiting for this mutex,
wake one of them up. */
futex_wake (mutex);
}
6.1.5 mcs spinlock
为了避免缓存一致性带来的开销, mcs spinlock 在 ticket spinlock 的基础上让每个 CPU 去检查自己的各自的变量
struct mcs_spinlock {
struct mcs_spinlock *next;
int locked; /* 1 if lock acquired */
int count; /* nesting count, see qspinlock.c */
};
static inline
void mcs_spin_lock(struct mcs_spinlock **lock, struct mcs_spinlock *node)
{
struct mcs_spinlock *prev;
/* Init node */
node->locked = 0;
node->next = NULL;
prev = xchg(lock, node);
if (likely(prev == NULL)) {
return;
}
WRITE_ONCE(prev->next, node);
/* Wait until the lock holder passes the lock down. */
arch_mcs_spin_lock_contended(&node->locked);
}
static inline
void mcs_spin_unlock(struct mcs_spinlock **lock, struct mcs_spinlock *node)
{
struct mcs_spinlock *next = READ_ONCE(node->next);
if (likely(!next)) {
/*
* Release the lock by setting it to NULL
*/
if (likely(cmpxchg_release(lock, node, NULL) == node))
return;
/* Wait until the next pointer is set */
while (!(next = READ_ONCE(node->next)))
cpu_relax();
}
/* Pass lock to next waiter. */
arch_mcs_spin_unlock_contended(&next->locked);
}
7 Parallelism
7.1 consistency
- memory consistency
- sequential consistency: overall effect consistent with each individual thread, arbitrary interleaving between threads
- non-coherent cache senario: may violate sequential consistency
- snoopy caches: tagged cahce line in main memory with its state (shared, exclusive), snoopy caches will get the correct copy of other threads' cache
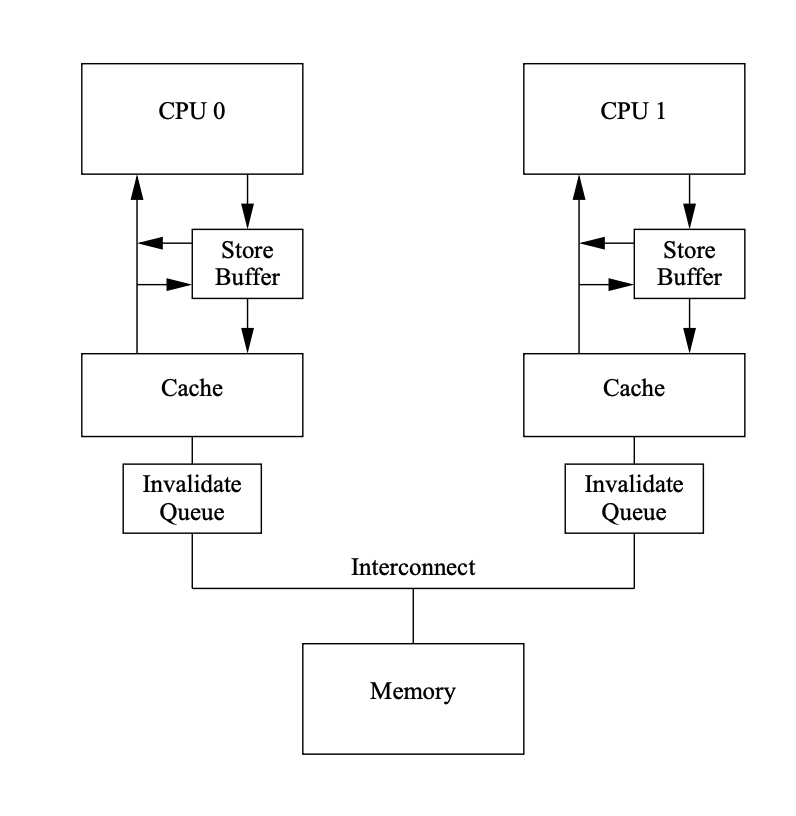
缓存一致性协议下的 CPU 缓存如图所示:
void foo() {
a = 1;
sfence();
b = 1;
}
void bar() {
while(b == 0) continue;
lfence();
assert(a == 1);
}
假设上面两个函数发生在两个 CPU 中:
- cpu foo 将 a 移入 store buffer
- cpu bar 将 a 移入 invalidate queue
- cpu foo 因为写内存屏障 sfence (store barrier) 将 store buffer 中的 a 刷入 cache line
- cpu foo 将 b 移入 cache line
- cpu bar 因为读内存屏障 lfence (load barrier) 将 invalidate queue 中的 a 清理
7.2 懒惰计数器 (sloppy counter)
懒惰计数器通过多个局部计数器和一个全局计数器来实现一个逻辑计数器, 局部计数器的值超过一个阈值 S (sloppiness) 时就把局部值转移到全局计数器, 局部计数器清零
每个 CPU 有自己的局部计数器, 不同 CPU 上的线程不会竞争
typedef struct counter_t {
int global; // global count
pthread_mutex_t glock; // global lock
int local[NUMCPUS]; // local count (per cpu)
pthread_mutex_t llock[NUMCPUS]; // ... and locks
int threshold; // update frequency
} counter_t;
// init: record threshold, init locks, init values
// of all local counts and global count
void init(counter_t *c, int threshold) {
c->threshold = threshold;
c->global = 0;
pthread_mutex_init(&c->glock, NULL);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < NUMCPUS; i++) {
c->local[i] = 0;
pthread_mutex_init(&c->llock[i], NULL);
}
}
// update: usually, just grab local lock and update local amount
// once local count has risen by 'threshold', grab global
// lock and transfer local values to it
void update(counter_t *c, int threadID, int amt) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->llock[threadID]);
c->local[threadID] += amt; // assumes amt > 0
if (c->local[threadID] >= c->threshold) { // transfer to global
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->glock);
c->global += c->local[threadID];
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->glock);
c->local[threadID] = 0;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->llock[threadID]);
}
// get: just return global amount (which may not be perfect)
int get(counter_t *c) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->glock);
int val = c->global;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->glock);
return val; // only approximate!
}
8 Persistence
8.1 I/O devices
- 设备接口包含 3 个寄存器: 状态 (status) 寄存器, 命令 (command) 寄存器, 数据 (data) 寄存器
操作系统轮询 (polling) 设备, 等待设备进入可以接收命令的就绪状态, 然后下发数据到数据寄存器 (programmed I/O,PIO), 操作系统将命令写入命令寄存器
While (STATUS == BUSY) ; // wait until device is not busy Write data to DATA register Write command to COMMAND register (Doing so starts the device and executes the command) While (STATUS == BUSY) ; // wait until device is done with your request
- CPU 不需要不断轮询设备, 设备完成了自身操作, 会抛出一个硬件中断触发 interrupt handler
- 设备在抛出中断之前往往会等待一小段时间, 将多次中断合并为一次中断抛出, 避免频繁的中断导致操作系统发生活锁 (livelock)
- DMA (Direct Memory Access) 可以协调完成内存和设备间的数据传递, 不需要 CPU 介入
8.2 file System
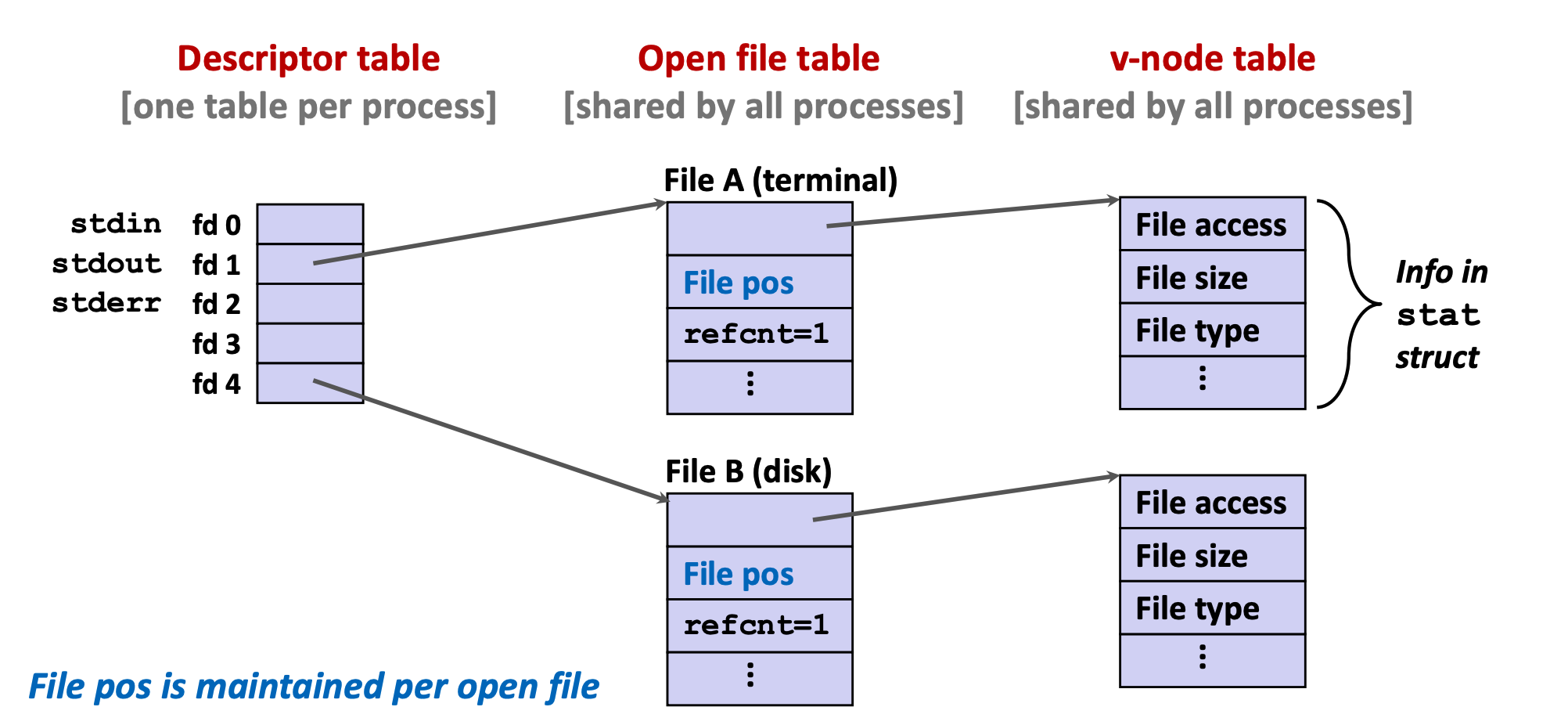
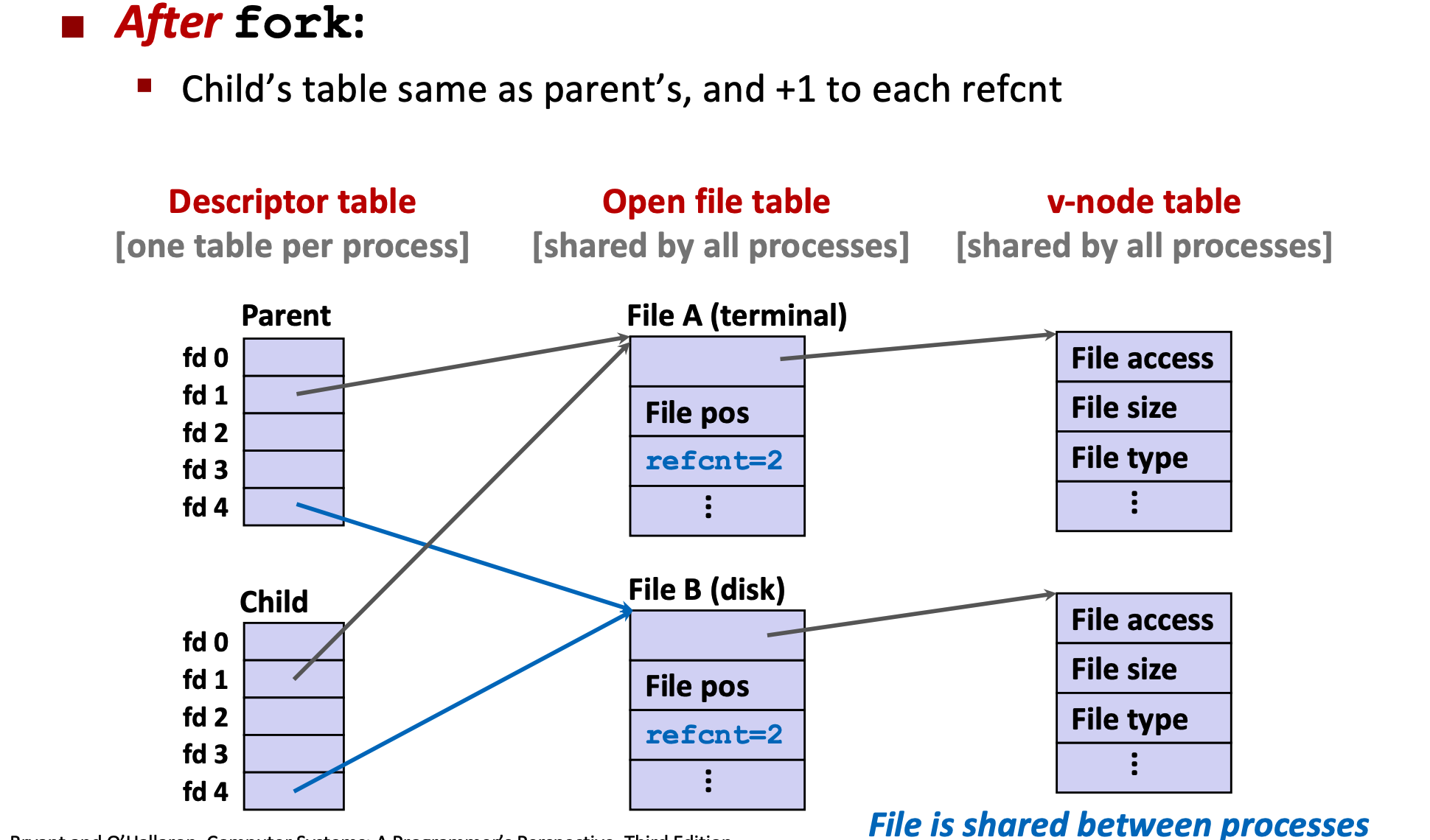
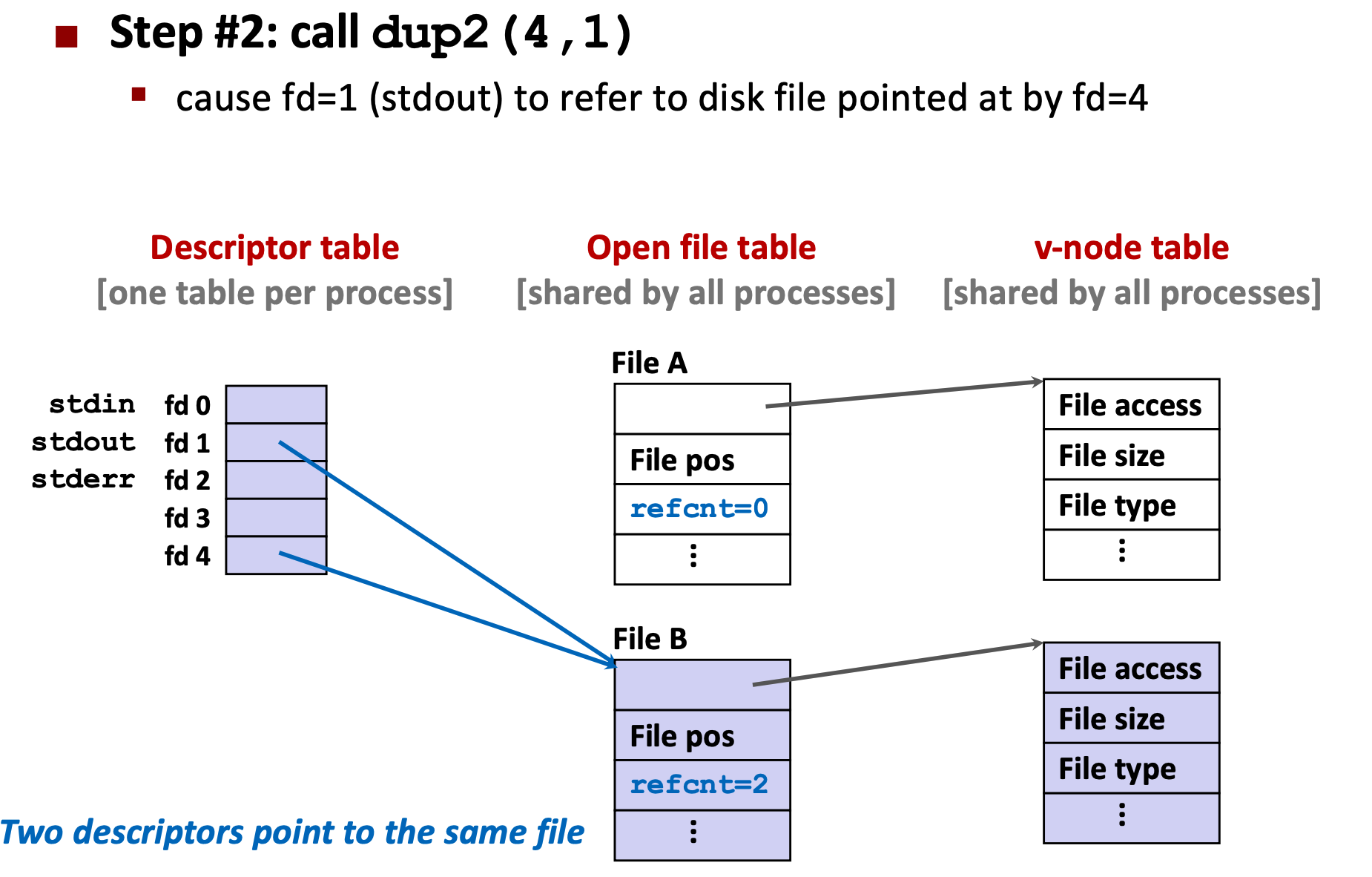
9 Network
9.1 socket
- struct sockaddr:
- sa_family (2 bytes - uint16_t) tells which protocol family it is
- sa_data (14 bytes) is the address data
struct sockaddr_in:
- sin_family (2 bytes) protocol family always AF_INET
- sin_port (2 bytes) port number in network bytes order (big endian order)
- sin_addr (4 bytes) IP address in network bytes order
- sin_zero (8 bytes) pad to sizeof(struct sockaddr)
- must cast sockaddr_in * to sockaddr * for functions
//ex: // _in 后缀是互联网络 (internet) 的缩写 struct sockaddr_in serverAddr; memset(&serverAddr, 0, sizeof(serverAddr)); // memset in <string.h> serverAddr.sin_family = AF_INET; serverAddr.sin_port = htons(5188); // htons in <arpa/inet.h> serverAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); bind(listenfd, (sockaddr*)&serverAddr, sizeof(serverAddr)) struct sockaddr_in peerAddr; connfd = accept4(listenfd, (sockaddr*)&peerAddr, &peerLength, SOCK_NONBLOCK | SOCK_CLOEXEC); std::cout << "ip = " << inet_ntoa(peerAddr.sin_addr) << "port = " << ntohs(peerAddr.sin_port) << std::endl;- AF = Address Family, PF = Protocol Family
9.2 send
syscall sendto 系统调用: 创建 msghdr, 发送 datagram 至给定的 sockaddr, 找到 socket, 将 sockaddr 移至内核空间 (sockaddr_storage), 在唤醒 protocol 前检查用户空间的数据为可读, 调用 sock_sendmsg
/* net/socket.c * SYSCALL_DEFINEx: x 代表参数的个数, 为了将32位参数先转成64位 * 解决 CVE-2009-2009 漏洞 */ SYSCALL_DEFINE6(sendto, int, fd, void __user *, buff, size_t, len, unsigned int, flags, struct sockaddr __user *, addr, int, addr_len) { return __sys_sendto(fd, buff, len, flags, addr, addr_len); }msghdr 结构体
/* include/linux/socket.h * struct sockaddr_storage address; * msg.msg_name = (struct sockaddr *)&address; */ struct msghdr { void *msg_name; /* ptr to socket address structure */ int msg_namelen; /* size of socket address structure */ struct iov_iter msg_iter; /* data */ /* * Ancillary data. msg_control_user is the user buffer used for the * recv* side when msg_control_is_user is set, msg_control is the kernel * buffer used for all other cases. */ union { void *msg_control; void __user *msg_control_user; }; bool msg_control_is_user : 1; __kernel_size_t msg_controllen; /* ancillary data buffer length */ unsigned int msg_flags; /* flags on received message */ struct kiocb *msg_iocb; /* ptr to iocb for async requests */ };sock_sendmsg
/* net/socket.c */ static inline int sock_sendmsg_nosec(struct socket *sock, struct msghdr *msg) { int ret = INDIRECT_CALL_INET(sock->ops->sendmsg, inet6_sendmsg, inet_sendmsg, sock, msg, msg_data_left(msg)); BUG_ON(ret == -EIOCBQUEUED); return ret; }transport layer inet_sendmsg
/* net/ipv4/af_inet.c */ int inet_sendmsg(struct socket *sock, struct msghdr *msg, size_t size) { struct sock *sk = sock->sk; if (unlikely(inet_send_prepare(sk))) return -EAGAIN; return INDIRECT_CALL_2(sk->sk_prot->sendmsg, tcp_sendmsg, udp_sendmsg, sk, msg, size); }tcp_sendmsg
/* net/ipv4/tcp.c */ int tcp_sendmsg(struct sock *sk, struct msghdr *msg, size_t size) { int ret; lock_sock(sk); ret = tcp_sendmsg_locked(sk, msg, size); release_sock(sk); return ret; }socket_lock_t
/* include/net/sock.h * This is the per-socket lock. The spinlock provides a synchronization * between user contexts and software interrupt processing, whereas the * mini-semaphore synchronizes multiple users amongst themselves. */ typedef struct { spinlock_t slock; int owned; wait_queue_head_t wq; /* * We express the mutex-alike socket_lock semantics * to the lock validator by explicitly managing * the slock as a lock variant (in addition to * the slock itself): */ #ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_LOCK_ALLOC struct lockdep_map dep_map; #endif } socket_lock_t;tcp_sendmsg_locked: 创建 sk_buffer (skb: sock buffer), 并加入 write_queue 的尾部, 然后调用 tcp_write_xmit 处理滑动窗口和拥塞控制, 再调用 tcp_transmit_skb 克隆新的 skb, 添加 tcp header, 调用 network layer 的发送接口
/* net/ipv4/tcp_output.c */ static bool tcp_write_xmit(struct sock *sk, unsigned int mss_now, int nonagle, int push_one, gfp_t gfp); static int tcp_transmit_skb(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb, int clone_it, gfp_t gfp_mask, u32 rcv_nxt); /* pass the packet down to IP */ err = icsk->icsk_af_ops->queue_xmit(sk, skb, &inet->cork.fl);network layer ip_queue_xmit: 检查 socket 中缓存的路由表, 没缓存则查找路由, 设置 ip header, 调用 ip_local_out ip_local_out: 调用 nf_hook 进行 netfilter(iptables 相关), 调用 dst_output(ip_output) ip_output: 进行 netfilter 后调用 ip_finish_output ip_finish_output: 大于 MTU 时进行分片, 最后调用 neigh_output
/* net/ipv4/ip_output.c */ int ip_queue_xmit(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb, struct flowi *fl, __u8 tos); int ip_local_out(struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb); int ip_output(struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb); static int ip_finish_output(struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb);link layer
- neighbour - neighbour/arp tables management 查找 arp 缓存或发送 arp 请求, 封装 MAC header
调用 dev_queue_xmit
netdev 把 skb 加入网卡的发送队列, 调用 __qdisc_run 开始发送
/* net/core/dev.c */ int dev_queue_xmit(struct sk_buff *skb);
__qdisc_run: quota 用尽或其他进程需要 CPU 时发送 NET_TX_SOFTIRQ 软中断
/* net/sched/sch_generic.c */ void __qdisc_run(struct Qdisc *q) { int quota = dev_tx_weight; int packets; while (qdisc_restart(q, &packets)) { quota -= packets; if (quota <= 0) { __netif_schedule(q); break; } } }qdisc_restart: 调用 dev_hard_start_xmit 驱动程序来发送数据
当触发软中断 NET_TX_SOFTIRQ 注册回调函数 net_tx_action, net_tx_action 通过 softnet_data 获取发送队列, 然后调用 qdisc_run
/* net/core/dev.c */ static __latent_entropy void net_tx_action(struct softirq_action *h);
- drivers igb_xmit_frame: skb 映射到 DMA 地址
发送完成 触发 NET_RX_SOFTIRQ 软中断
/* net/core/dev.c */ static inline void ____napi_schedule(struct softnet_data *sd, struct napi_struct *napi) { list_add_tail(&napi->poll_list, &sd->poll_list); __raise_softirq_irqoff(NET_RX_SOFTIRQ); }回调函数清理 skb 和 ring buffer, 解除了 DMA 映射, 接收到 ack 后 skb 完全清理
9.3 receive
- 到达网卡
- 通过 DMA 把数据写入 ring buffer
触发硬中断(网卡的硬中断注册的处理函数是 igb_msix_ring)
/* net/ethernet/intel/igb/igb_main.c */ static irqreturn_t igb_msix_ring(int irq, void *data) { struct igb_q_vector *q_vector = data; /* Write the ITR value calculated from the previous interrupt. */ igb_write_itr(q_vector); napi_schedule(&q_vector->napi); return IRQ_HANDLED; }修改 poll_list 触发软中断 NET_RX_SOFTIRQ
- 软中断回调函数 调用驱动的 poll 函数收包, 将收到的包送到协议栈注册的 ip_rcv, 再送到 tcp_rcv
9.4 tcp
- 一条 TCP 连接的双方均可随机地选择初始序号, 这样做可以减少将旧连接 (使用同样的端口号 SO_REUSEADDR) 发送的报文误认为是新连接的
- TimeoutInterval = EstimatedRTT + 4 * DevRTT, RTT 估计值和偏差值通过指数加权移动平均 (Exponential Weighted Moving Averge, EWMA) 计算
- duplicate ACK 冗余 ACK: 接收方对已经接收到的最后一个按序字节数据进行重复确认产生, 发送方一旦接受到 3 个冗余 ACK, TCP 就执行快速重传 (fast retransmit)
- TCP 的差错恢复机制为 go-back-N 和 selective repeat 的混合, 接收方有选择地确认失序报文段
- 丢包事件的定义: 出现超时 或者 收到来自接收方的 3 个冗余 ACK, 出现过度的拥塞时, 路径上的一台或多台路由器的缓存会溢出, 导致丢包
- 慢启动
- TCP 连接开始时, cwnd 初始值为一个 MSS, 每接收到一个 ACK 就增加一个 MSS, 这导致每过一个 RTT 就翻倍
- 当遇到一个 timeout 丢包事件, 设置慢启动阈值 ssthresh 为 cwnd/2, 将 cwnd 设置为 1, 重新开始慢启动过程, 当检测到 cwnd 到达 sshthresh 时, 结束慢启动并转移到拥塞避免模式
- 当遇到一个冗余 ACK 为 3 的丢包事件, 执行一次快速重传, cwnd 减半, 结束慢启动并进入快速恢复模式
- 拥塞避免
- 每个 RTT 增加一个 MSS, 可通过每个 ACK 增加 1/n 个 MSS 实现
- 出现 timeout: ssthresh 设为 cwnd/2, cwnd 设为 1, 进入慢启动
- 出现 3 duplicate ack: ssthresh 设为 cwnd/2, cwnd 减半, 进入快速恢复
- 快速恢复
- 对于每个冗余 ACK, 增加一个 MSS, 进入拥塞避免
- 出现 timeout: ssthresh 设为 cwnd/2, cwnd 设为 1, 进入慢启动
- TCP 拥塞控制被称为加性增, 乘性减 Additive-Increase, Multiplicative-Decrease AIMD
- tcp backlog
- 第二次握手: 服务端发送完 SYN/ACK 后在内存中建立 SYN-RECEIVED 的连接,将连接放进 incomplete connection queue, 最大长度为 /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_max_syn_backlog (1024)
- 关闭 syncookies(net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 0), 当队列满时, 不再接受新的连接
- 开启 syncookies(net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1), 当队列满时, 不受影响
- 当服务端发送 SYN/ACK 后将会开启一个定时器, 如果超时没有收到客户端的 ACK, 将会重发 SYN_ACK 包, 重传的次数由 /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_synack_retries 控制, 默认是5次
第三次握手: 服务端收到 ACK 后, TCP 连接进入 ESTABLISHED 状态, 将连接放进 complete connection queue, 等待应用程序进行 accept, 其最大长度为 listen 函数的参数 backlog 和 /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn (128) 的较小值
int listen(int sockfd, int backlog); // backlog 参数暗示了内核在开始拒绝连接请求之前, 队列中要排队的未完成的连接请求的数量, 一般为 128 listen(listenfd, SOMAXCONN);
- 当 sysctl_tcp_abort_on_overflow 为 0 时, Linux 内核只丢弃客户端的 ACK 包, 然后什么都不做
- 当 sysctl_tcp_abort_on_overflow 非 0 时, Linux 内核会返回 RST 包, reset TCP 连接
- ss -lnt : Send-Q 表示全连接队列大小的最大值, Recv-Q 表示全连接队列的使用大小
- netstat -s : the listen queue of a socket overflowed 全连接队列溢出次数, SYNs to LISTEN sockets dropped 半连接队列溢出次数
- netstat -t (Established): Send-Q 表示发送队列中没有被远程主机确认的 bytes, Recv-Q 表示在缓存中没被进程读取 bytes
- 第二次握手: 服务端发送完 SYN/ACK 后在内存中建立 SYN-RECEIVED 的连接,将连接放进 incomplete connection queue, 最大长度为 /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_max_syn_backlog (1024)
10 Daemon Processes
创建一个守护进程的步骤:
- clear file creation mask: umask(0)
- fork 子进程, 父进程退出
- become a session leader to lose controlling TTY: setsid()
- ensure future opens won't allocate controlling TTYs: ignore SIGHUP
- fork 子进程, 父进程退出
- change the current working directory to the root: chdir("/")
- close all open file descriptors: close(i) i 从0到 rlim_max
- attach file descriptors 0, 1, and 2 to /dev/null: open("/dev/null", O_RDWR)
- initialize the log file: openlog, syslog
经过以上步骤, 这个守护进程在孤儿进程组中 (PPID 为1), 不是会话首进程 (不会被分配到一个控制终端)
11 Interprocess Communication
- 管道: 半双工, 只能在具有公共祖先的两个进程之间使用
Unix domain socket: 全双工, 可以使用 bind(2), listen(2), accept(2), connect(2)
#define UNIX_PATH_MAX 108 struct sockaddr_un { __kernel_sa_family_t sun_family; /* AF_UNIX */ char sun_path[UNIX_PATH_MAX]; /* pathname */ };
11.1 POSIX shared memory
#include <sys/mman.h> #include <sys/stat.h> /* For mode constants */ #include <fcntl.h> /* For O_* constants */ int shm_open(const char *name, int oflag, mode_t mode); int shm_unlink(const char *name); int ftruncate(int fd, off_t length); void *mmap(void *addr, size_t length, int prot, int flags, int fd, off_t offset); int munmap(void *addr, size_t length);
共享内存通常和环形缓冲配合使用
11.1.1 ring buffer
环形缓冲的结构如下, kfifo 结构体和 data 数据均通过 kmalloc 创建, in 表示写的位置, out 表示读的位置
struct __kfifo {
unsigned int in;
unsigned int out;
unsigned int mask;
unsigned int esize;
void *data;
};